Unlocking FX Investments: Determinants of Currency Rates, and Trading With Bybit MT5
Key Takeaways:
Diverse Investment Options: FX investments encompass various instruments, such as spot transactions, forward contracts, currency options and ETFs. A groundbreaking new form of FX trading is through Bybit’s MT5.
Impact of Interest Rates and Inflation: Interest rates and inflation are crucial determinants of currency value. Rising inflation typically leads central banks to increase interest rates as they seek to stabilize their economies, affecting demand for their respective currencies. Conversely, high inflation can erode a currency's value, making it essential for traders to understand these dynamics.
Market Influencers: The FX market is also influenced by other factors, including economic indicators (such as GDP and unemployment rates), political events and market sentiment.
Introduction to FX Investments
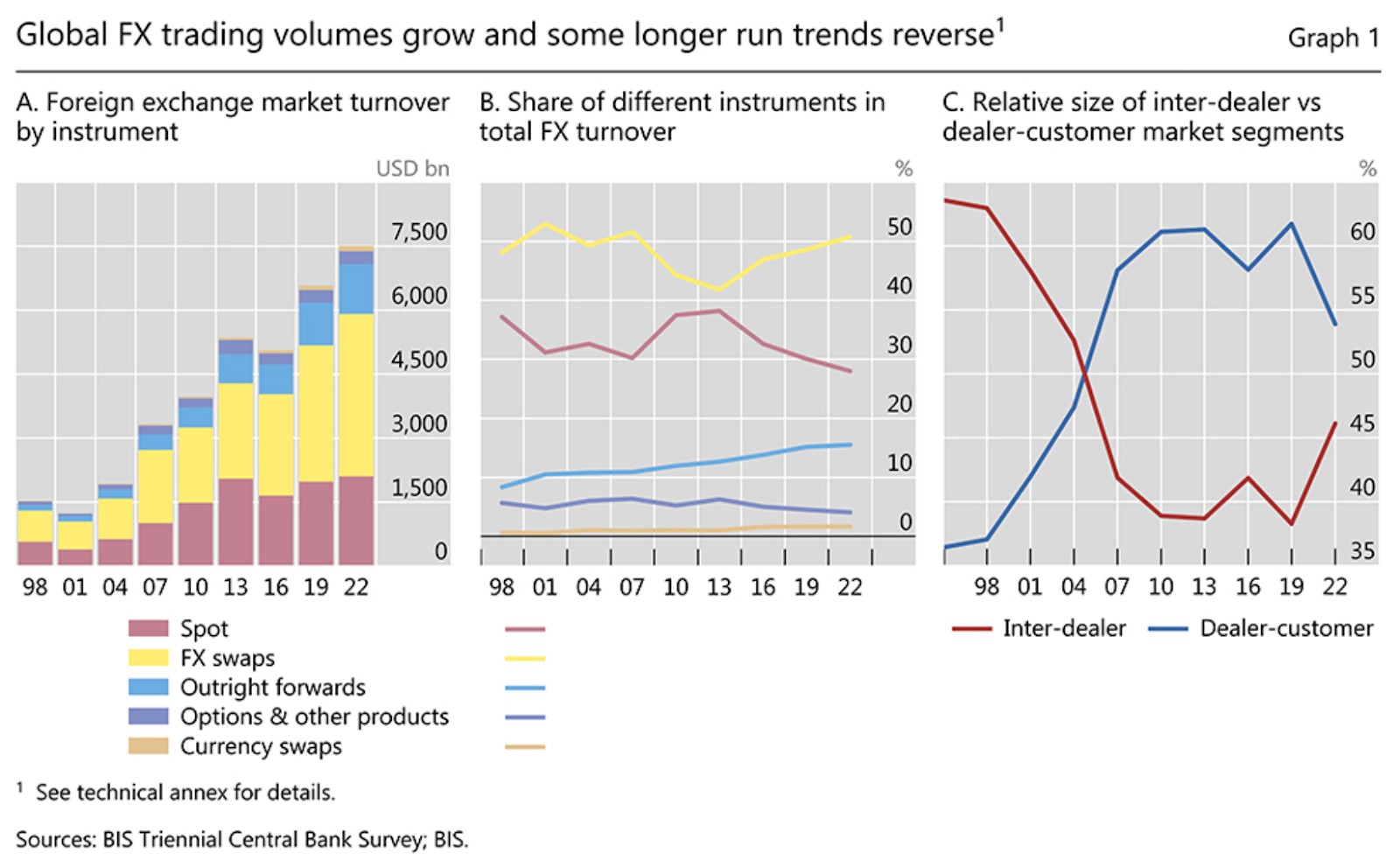
Foreign exchange (FX) investments involve trading currencies in the foreign exchange (forex) market, the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7.5 trillion. Investors engage in FX trading for various reasons, including speculation, hedging against currency risk and portfolio diversification. Understanding the mechanics of FX investments and the factors that determine exchange rates is crucial for effective trading strategies.
Traditional FX Investments
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. This is the most straightforward form of FX trading, with trades typically settled within two business days. Spot prices fluctuate continually based on supply and demand dynamics in the market.
Forward Contracts
A forward contract is an agreement to exchange a specific amount of currency at a predetermined rate on a set future date. This type of instrument allows investors to hedge against unfavorable currency movements. For example, a company expecting to receive payments in a foreign currency can lock in an exchange rate to protect its profit margins.
Currency Options
Currency options provide investors with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price before or on a specific date. Options can be used for hedging or speculative purposes, allowing flexibility in trading strategies. For instance, an exporter might use a currency option to protect against a decline in the value of the currency they’ll receive.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Currency-focused ETFs allow investors to gain exposure to FX markets without directly trading currencies. These types of funds track the performance of a specific currency (or a basket of currencies), making them an accessible option for those looking to diversify their portfolios.
Futures Contracts
Futures contracts are standardized agreements that obligate the buyer to purchase (and the seller to sell) a specific amount of currency at a set price on a future date. Although these types of contracts are similar to forward contracts, they’re regulated and traded on exchanges, providing more transparency and liquidity.
Currency Swaps
In a currency swap, two parties exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies. This can be an effective way for companies to manage currency exposure and facilitate cross-border financing.
Trade With Bybit MetaTrader 5
For crypto enthusiasts, there’s great news: you can now trade gold directly on Bybit! Bybit MetaTrader 5 provides access not only to cryptocurrencies and forex, but also to contracts for difference (CFDs). Following are the exceptional benefits offered by MT5 on Bybit:
500x Leverage: Unlock the potential to amplify your trading opportunities with leverage of up to 500x.
0-Pip Spreads: Take advantage of ultra-low spreads to enhance your potential returns.
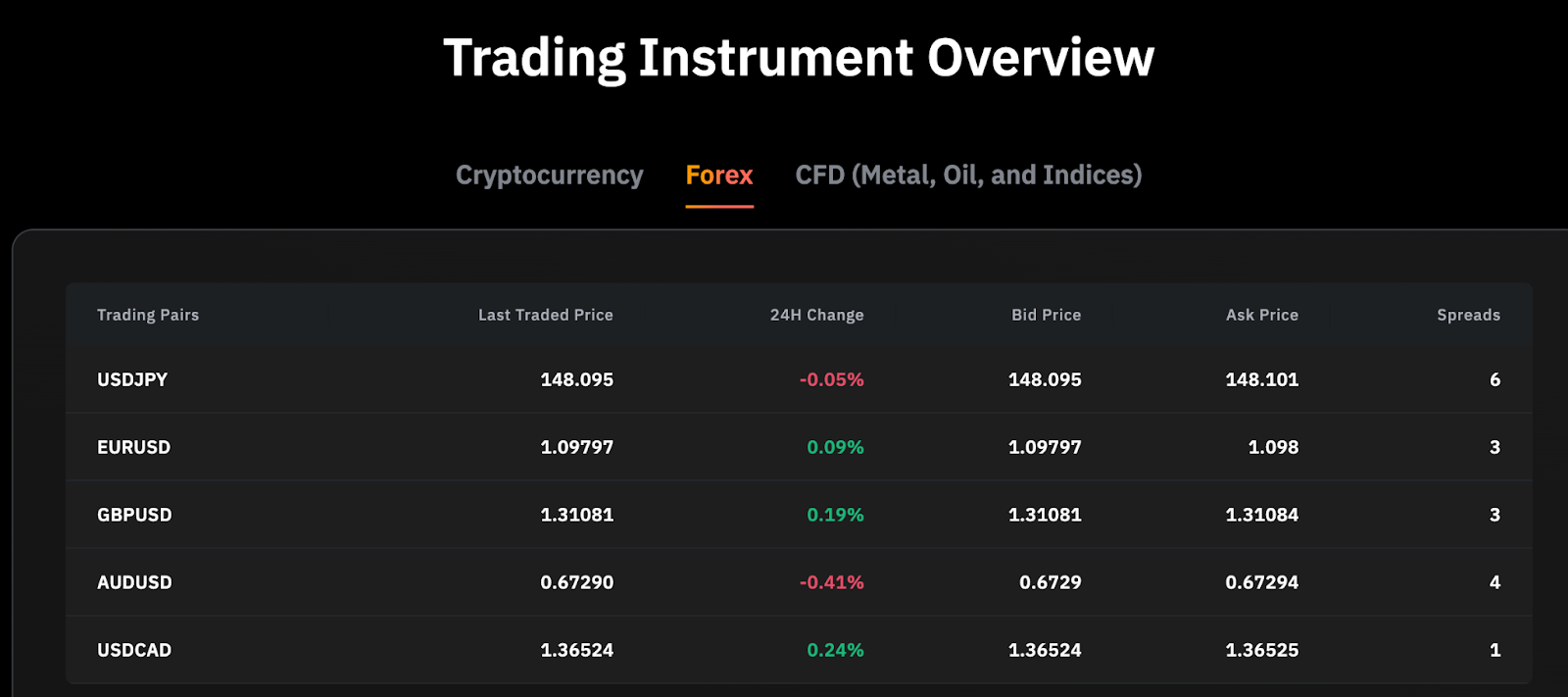
100+ Popular Trading Pairs: Explore a wide range of financial instruments on Bybit's MT5 platform, including forex, cryptocurrencies, commodities and stock indices.
Customizable Fees: Enjoy zero fees for closing positions, with trading fees starting as low as 3 basis points. For forex and CFD instruments, minimum closing fees begin at just $3 per lot, alongside exclusive VIP rates.
Top-Tier Liquidity: Experience efficient trade execution on our high-volume exchange platform, ensuring best-in-class liquidity and market depth to minimize price impacts during trades.
24/7 Customer Support: Get your questions answered around the clock by our multilingual customer support team, who are ready to provide you with exceptional assistance whenever needed.
Determinants of FX Rates
FX rates are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, broadly categorized into economic indicators, market sentiment, geopolitical events and central bank policies.
Interest Rates
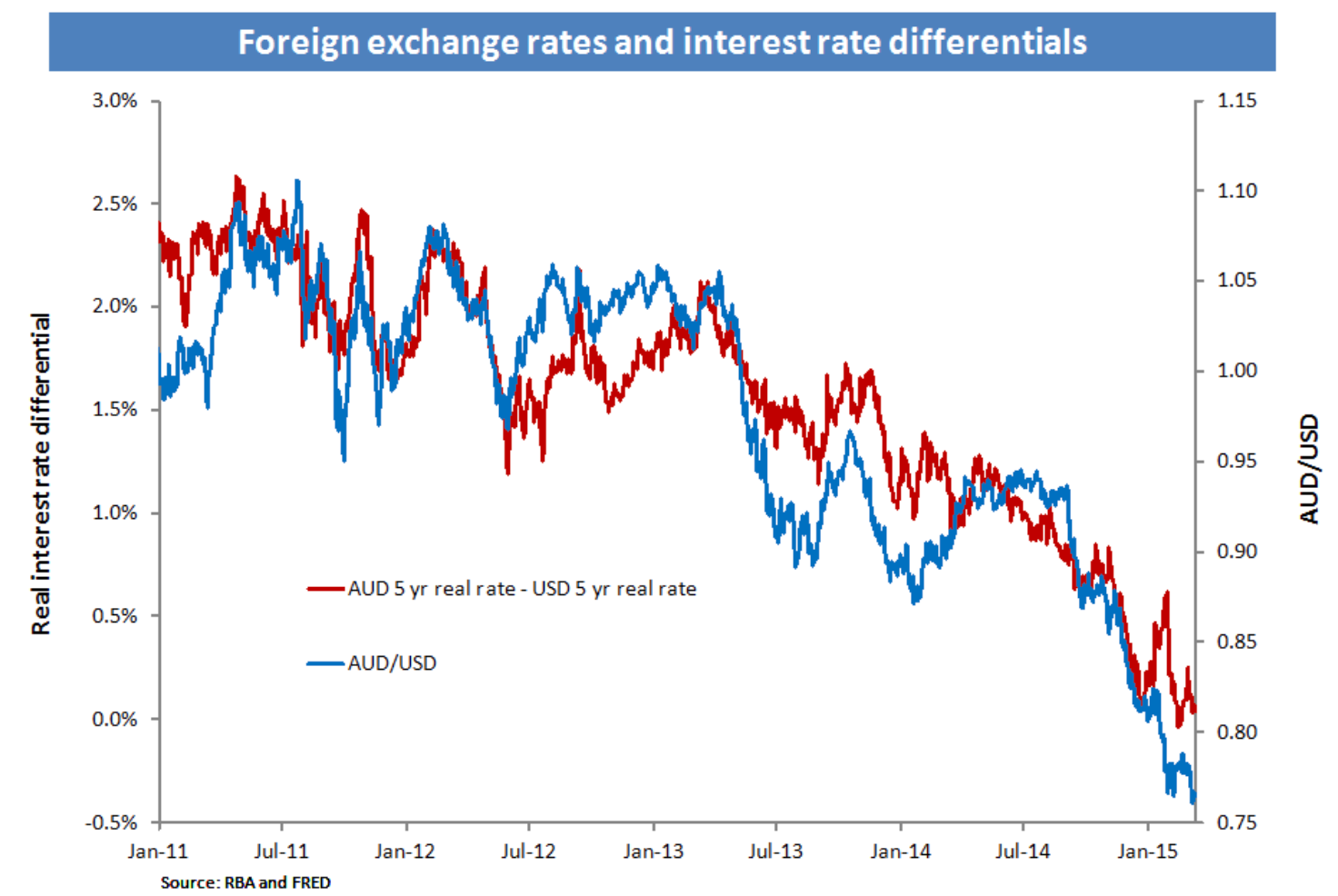
Interest rates are a critical factor in determining currency’s perceived value, highlighting the importance of understanding how central banks set monetary policy. Inflation significantly influences these decisions, as moderate inflation is linked to economic growth, while excessive inflation can lead to rate adjustments that impact currency strength. Interest rate hikes generally slow economic growth, but they also strengthen the currency, whereas interest rate cuts encourage borrowing and spending.
Traders focus more on expected future interest rates than on current rates, anticipating shifts in monetary policy that could signal currency movements. Interest rate differentials are also crucial, as an increasing differential typically favors the higher-yielding currency, while a narrowing one supports the lower-yielding currency. Additionally, the distinction between nominal and real interest rates is important, with markets prioritizing real rates that account for inflation.
Finally, sudden changes in economic reports can drastically alter interest rate expectations and currency values, making it essential for traders to remain informed about financial news.
Inflation Rates
Inflation affects purchasing power and currency value. Low inflation rates typically correlate with a stronger currency, as they indicate stable economic conditions. Conversely, high inflation can erode a currency’s value. For instance, if the U.S. experiences rising inflation while the Eurozone remains stable, the U.S. dollar may weaken against the euro.
Interest rates and inflation are closely linked, impacting currency values in the forex market. When inflation rises, central banks typically increase interest rates to control price levels and stabilize the economy. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can reduce consumer spending and investment, ultimately slowing economic growth. However, such an environment attracts foreign investors seeking higher returns, leading to increased demand for the domestic currency. For instance, in India, a rise in interest rates can boost the value of the Indian rupee as foreign investors convert their currencies to invest locally.
Recent Trends in India
Consider the inflation spike in India, which has resulted in a significant depreciation of the Indian rupee against major currencies. Traders who anticipated this trend and adjusted their portfolios accordingly achieved substantial profits. The following table illustrates how interest rate adjustments correlate with currency value changes during inflationary periods.
Time Period | Inflation Rate | Interest Rate Adjustment | Currency Value Change |
2023 Q2 | 6.5% | +0.75% | +2.3% |
2023 Q3 | 8.2% | −0.50% | −1.8% |
2023 Q4 | 7.1% | +1.20% | +3.5% |
Inflation's Impact on Forex Rates
The relationship between inflation and currency values is generally inverse. Higher inflation levels can diminish a currency's competitiveness in global markets, leading to a decline in demand for that currency. For example, if India's inflation rate is 5% while Russia's is 2%, India's real exchange rate would be 3% higher than Russia's, even if nominal rates remain unchanged.
Economic Indicators
Key economic indicators provide insights into a country's economic health, and also influence FX rates.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Strong GDP growth generally leads to currency appreciation as it signals economic strength.
Unemployment Rates: Lower unemployment often correlates with stronger economic performance, and can boost currency value.
Manufacturing and Services Data: Economic surveys and indices such as PMI (Purchasing Managers' Index) offer insights into economic activity and can impact currency perception.
Supply and Demand
The fundamental economic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role in how trade balances influence currency exchange rates. When a country experiences a trade surplus, this indicates that demand for its goods and services is exceeding that in other countries. The resulting heightened demand for the nation's currency increases its value relative to other currencies. On the other hand, a trade deficit suggests lower demand for the country's currency, which can lead to a decline in its value.
Political Stability and Economic Performance
Countries with political stability and sound economic policies attract foreign investment. Political uncertainty — such as fraught elections or governmental instability — can lead to currency depreciation as investors seek safer assets. For example, political turmoil in a country can lead to capital flight, weakening its currency.
Market Sentiment
Traders’ perceptions play a significant role in FX markets. Sentiment can be influenced by news events, economic reports and geopolitical developments. Positive sentiment can drive demand for a currency, while negative news can lead to sell-offs.
Global Events
Geopolitical events, economic crises and natural disasters can create volatility in FX markets. For instance, tensions in the Middle East or economic downturns can lead investors to seek safe-haven currencies, such as the U.S. dollar or Swiss franc, impacting exchange rates.
Key Participants in FX Markets
Central Banks: Central banks play a critical role in FX markets, influencing currency values through monetary policy and direct market interventions. For example, the Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions can significantly impact the strength of the U.S. dollar.
Commercial Banks: Commercial banks are major players in the FX market, acting as market makers. They facilitate currency exchanges for clients and engage in proprietary trading to profit from currency fluctuations.
Hedge Funds and Institutional Investors: Hedge funds and institutional investors actively trade currencies, often using sophisticated strategies and large amounts of capital to exploit market inefficiencies. Their trading activity can lead to significant price movements in forex markets.
Corporations: Multinational corporations engage in FX trading to manage currency risk associated with international operations. They often use hedging techniques to protect profit margins from adverse currency movements.
Retail Investors: Retail investors participate in FX markets through brokerage platforms, using leverage to amplify their trading potential. While they make up a small portion of the overall market, their collective activity can nevertheless influence price trends.