Explained: What Is Litecoin (LTC) and How Does It Work?
Little more than a decade has passed since the cryptocurrency market first emerged. Its growth has been exponential, with the market capitalization of Bitcoin alone surpassing $524 billion as of May 23, 2023. Even with the creation of thousands of cryptocurrencies aimed at solving various problems, Bitcoin has continued to dominate the market.
Nevertheless, some older altcoins, such as Litecoin, are still in use today, despite debates about their antiquated concept. Litecoin has recently attracted the market's attention once again due to its upcoming halving event.
Despite its lack of support for smart contracts, and characteristics largely similar to those of Bitcoin, Litecoin has remained in the top 20 cryptos in terms of market capitalization. More recently, Litecoin has managed to overtake Polkadot (and meme coin Shiba Inu) to claim number 13 on the list.
What is Litecoin — and why has its valuation remained so high among thousands of other cryptocurrencies? In this article, we’ll discuss what Litecoin is, its history and how it works.
Key Takeaways:
- Litecoin is an open-source global peer-to-peer cryptocurrency network that enables users to send payments worldwide in a fast and affordable manner.
- The upcoming Litecoin halving event is likely to be held on Aug 3, 2023, and will decrease mining rewards to 6.25 LTC per completed block.
- Bybit offers the LTC/USDT Spot pair and LTCUSDT Perpetual Contracts for trading.
What Is Litecoin (LTC)?
Litecoin is an open-source global peer-to-peer (P2P) cryptocurrency network that enables users to send payments worldwide in a fast and affordable manner.
The Litecoin network was founded on Oct 13, 2011, and was originally created as a fork of Bitcoin (BTC) to improve on three main issues faced by the Bitcoin network — speed, scalability and centralization.
Litecoin is designed to be an ideal digital assets payment method for merchants and consumers, providing instant transaction confirmations. It uses a proof of work (PoW) consensus to secure the network, similar to Bitcoin. However, the hashing algorithm used by its network is different from that of Bitcoin. Litecoin uses Scrypt, while Bitcoin uses SHA-256. This will be discussed in more detail.
Litecoin Halving
Whenever miners complete a block, they earn LTC rewards. However, as with Bitcoin halving, the mining rewards for Litecoin decrease over time. This mechanism is built into the Litecoin protocol to control the issuance rate and ensure a limited supply of the cryptocurrency. Based on the previous halving event on Aug 5, 2019, Litecoin now offers 12.5 LTC per completed block. The next halving event will take place around Aug 3, 2023, and will decrease mining rewards to 6.25 LTC per completed block.
The upcoming Litecoin halving event has generated significant buzz and anticipation within the cryptocurrency community, especially since it’s just a couple of months away. Scheduled to occur at regular intervals of approximately four years, the halving event is an integral part of Litecoin's monetary policy.
The primary implication of the Litecoin halving event is a reduction in the rate at which new Litecoins are created. This scarcity mechanism is designed to curb inflation by providing a deflationary aspect to the cryptocurrency. With each halving, the reward for miners diminishes, which may potentially impact their profitability. Consequently, this event has been known to trigger changes in the mining landscape, as miners reevaluate their strategies and assess the viability of their operations.
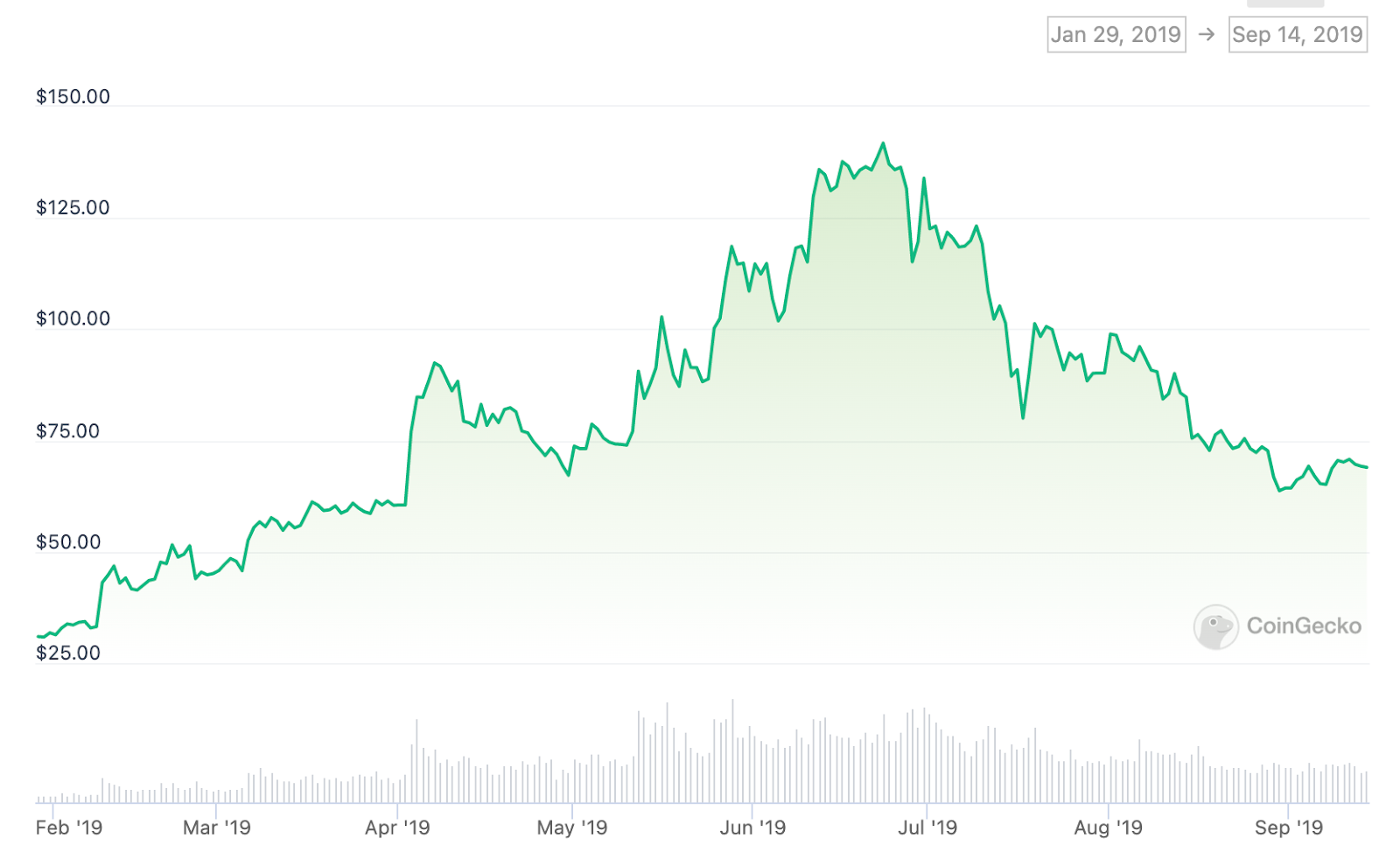
Historically, Litecoin halving events have had significant effects on the price and market sentiment surrounding the cryptocurrency. For example, in the months preceding its 2019 halving event, LTC price experienced a surge, growing from $30 in January to a high of $141.82 on Jun 23, 2019.
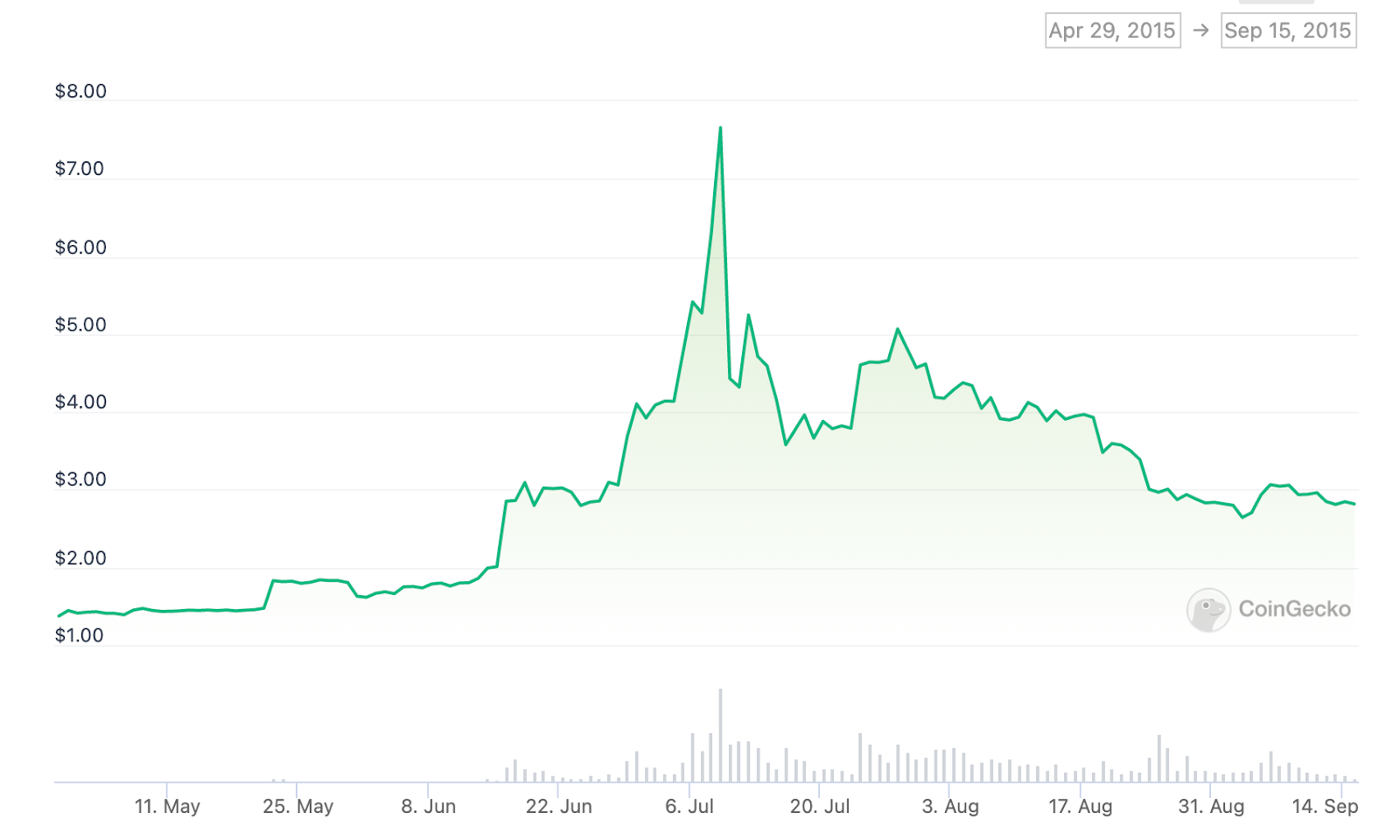
Likewise, before its 2015 halving event, LTC price rose from a low of $1.45 in May to $7.66 on Jul 9, 2015.
Does Past Performance Indicate Future Results?
Previous halvings have often been associated with bullish trends, as reduced supply coupled with sustained demand has led to upward price movements. However, it’s crucial to note that past performance is not indicative of future results, and the cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and influenced by numerous factors.
As the next Litecoin halving event approaches, market participants and enthusiasts are eagerly observing its potential impact. Traders and investors closely monitor price movements and analyze market conditions to gauge the short- and long-term implications of the halving.
Additionally, the event often generates renewed interest in Litecoin, attracting newcomers to the cryptocurrency space who wish to capitalize on potential price surges or explore the technology behind this established digital asset.
The upcoming Litecoin halving event represents an important milestone in the cryptocurrency's journey. The event's effects on mining profitability and market sentiment remain to be seen, but it is undoubtedly capturing the attention of the cryptocurrency community as they await the next chapter in Litecoin's development.
Properties of Litecoin
Litecoin was specifically designed to reduce the amount of time it takes to validate a new block, and to uphold storage efficiency. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of its properties.
Transaction Speed
Litecoin has a transaction processing speed of 54 TPS, which is significantly higher than Bitcoin’s transaction processing speed of 5 TPS.
Scalability
The block mining time for Litecoin is two and a half minutes, which is four times faster than the ten minutes it takes for Bitcoin to generate blocks. As a result, Litecoin’s network is able to achieve a higher throughput.
Decentralization
The Scrypt hashing algorithm is used to power Litecoin’s PoW consensus mechanism, giving the network a lower barrier to entry and allowing more individuals to participate in the Litecoin mining process.
This contributes to the network’s decentralization, given that mining power is no longer concentrated among bigger players who can afford expensive equipment such as application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) miners.
Transaction Fees
The fee structure of Litecoin is 1/50th the size of Bitcoin’s, which drastically reduces transaction costs.
Security
Litecoin’s Scrypt hashing is designed to be more secure than alternative functions against hardware brute-force attacks. Even after a decade, Litecoin hasn’t suffered any major exploits, demonstrating its reliability as a cryptocurrency.
Privacy
Litecoin is also a privacy cryptocurrency. The MWEB (MimbleWimble Extension Block) upgrade allows users to opt in as necessary to conduct private transactions, and transaction anonymity is guaranteed — so that a transaction amount is known only to the sender and receiver.
Read here to learn more about how Litecoin remains among the top 20 cryptocurrencies even after a decade.
Who Founded Litecoin Crypto?
Litecoin was founded in October 2011 by Charlie Lee, a computer science graduate of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and former Google employee. Addressing Bitcoin’s slow transaction speed and lack of scalability, Lee decided to create a “lighter” version of Bitcoin that would facilitate faster transactions and greater scalability, along with lower transaction fees.
In 2013, Lee joined Coinbase as the Director of Engineering. When this news reached the market, the price of Litecoin increased tenfold, from $3 to $30.
When Litecoin's price peaked at €300 in December 2017, Lee sold off all of his holdings, undermining investor confidence and sparking rumors of Litecoin price manipulation. However, Lee made it clear that his concern for a potential conflict of interest as a result of his growing influence over Litecoin was the reason for his actions. More details can be found here.
Lee left Coinbase in 2017, and is currently heading the Litecoin Foundation, focused on the development of Litecoin.
How Does Litecoin Work?
Like Bitcoin, Litecoin operates on an open-source blockchain that isn't under the control of a single central authority. To ensure that new Litecoin transactions don’t contradict the blockchain's transaction history, each Litecoin node operator has a copy of every blockchain, and miners assist in processing new transactions by including them in recently mined blocks.
Supply
Litecoin has a hard cap of 84 million LTC on its total supply (four times that of Bitcoin).
Orphaned Blocks
Litecoin mining can result in orphaned blocks. When two miners complete a block at nearly the same time and the chain initially accepts both, but later rejects one, orphaned blocks are created. The low block confirmation time results in a large number of orphaned blocks. The Segregated Witness (SegWit) protocol tackles this problem and reduces the number of orphaned blocks.
Scrypt Hashing Algorithm
Litecoin uses a hashing algorithm called Scrypt. The Litecoin development team initially chose Scrypt to prevent ASIC miners from controlling mining. ASIC mining was initially less suited to the Scrypt mining algorithm's higher memory requirements, which increased opportunities for other miners, including those who used CPU and GPU technology. However, ASIC-based mining with Scrypt support has evolved over time. Therefore, due to inferior computational capabilities, CPU- and GPU-based miners no longer possess useful LTC mining equipment, as ASICs produce significantly more hashes per second.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic Swaps facilitate the exchange of cryptocurrencies on different blockchains, or cross-chain trading. This adds interoperability to the Litecoin blockchain.
Avoiding Pre-Mine
A pre-mine, which enables the developers of a blockchain-based cryptocurrency to mine coins before the project is made public, was largely avoided with Litecoin. Pre-mining was initially used to pay the project's founders and finance its creation.
Many community members at the time desired alternative currencies with a fair launch, similar to that of Bitcoin. When Litecoin first launched, Lee addressed these issues, stating that it’s "against the decentralized vision of Bitcoin" for one person or group to control a significant number of coins and use them however they see fit.
One week prior to Litecoin going live, Lee made its source and binary codes available so that users could test mine it. A poll on the Bitcointalk forum was used to choose the time of launch so that users could select the time that best suited them. Since everyone was aware of the launch date, and only needed to make a small change to their files to begin mining actual Litecoin, everyone was able to mine simultaneously.
However, Litecoin still had a modest pre-mine. The genesis block — that is, the first one on the network — was pre-mined with a total of 150 LTC, with two additional blocks mined to confirm its validity. The reward for mining one block when Litecoin first launched was 50 LTC, which was essentially worthless at the time.
How to Mine Litecoin
Mining
In a blockchain, transaction data is stored in blocks. The block is made available to any system participant (referred to as a miner) who requests to see it. Litecoin miners verify the block by using mining software to solve difficult mathematical puzzles, in order to be granted permission to add new transactions to the blockchain. After a miner confirms the block, it’s added to the blockchain and the miner is rewarded with LTC.
Setting Up Mining Equipment
Litecoin can be mined using ASIC mining devices with pre-installed mining software. On the other hand, if you're mining with a CPU or GPU you must choose your own program, while keeping security in mind. A software product might contain malware, and other shady, if not malicious, activities should also be on your radar.
Choice of Mining
Once you've chosen your mining equipment, you’ll need to decide whether to mine alone or in a group. If you mine by yourself, you run the risk of going a long time without finding a block. However, if you succeed, you keep the entire LTC block reward, plus fees. Keep in mind that you can only achieve this if you have sufficient hash power, which requires multiple ASICs.
Furthermore, if you use a GPU or CPU to mine LTC on your own, there’s almost no chance that you’ll ever make any money. The benefits of pool mining outweigh those of solo mining, but the rewards are divided among the pool members according to the hash power they’ve contributed.
Litecoin vs. Bitcoin vs. Ethereum
As of May 23, 2023, the two largest cryptocurrencies in the market are Bitcoin and Ethereum, accounting for 44.47% and 18.68% of total cryptocurrency market capitalization, respectively.
There are specific differences between Litecoin, Bitcoin and Ethereum, particularly in terms of consensus mechanism, security and scalability. To learn more, please refer to this article.
Where to Buy Litecoin
You can trade Litecoin on most cryptocurrency exchanges, including Bybit. Bybit offers both the LTC/USDT Spot pair and LTCUSDT Perpetual Contracts. You can buy LTC with the USDT stablecoin via a Perpetual contract with leverage. Simply fund your verified account with USDT, or first convert another cryptocurrency to USDT.
Sign up for a Bybit account now and start trading!
Closing Thoughts
Even though Litecoin has been overshadowed by Bitcoin, it still ranks among the top 20 cryptocurrencies — even as thousands of new cryptos have been added. This is a good indicator of LTC’s strength. Furthermore, with the upcoming halving event, Litecoin is likely to gain even more traction in the crypto market. Given the highly capable technical team behind Litecoin, we can certainly look forward to seeing continued development and innovation. That said, we would still recommend you do your own research before investing any of your money in cryptocurrencies.
#Bybit #TheCryptoArk